Renewable power sources are pivotal in our quest for a sustainable future. This comprehensive guide delves into the primary sources of renewable power and offers actionable strategies for integrating sustainability into daily life.
Harnessing the Sun’s Power
Solar power, derived from the sun’s rays, is a cornerstone of renewable power. Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity, offering a clean, abundant energy solution.
The scalability of solar panels, from rooftop installations to vast solar farms, underscores their versatility in different settings. Solar energy’s benefits extend beyond electricity generation; solar thermal technology, for instance, uses sunlight to heat water and spaces in buildings.
The global embrace of solar technology is reducing dependence on fossil fuels. However, challenges persist. The efficiency of solar panels can fluctuate based on weather and location, necessitating advancements in storage technology to ensure a steady power supply. Check out this site for more info on solar panels and renewable energy sources.
Wind Energy
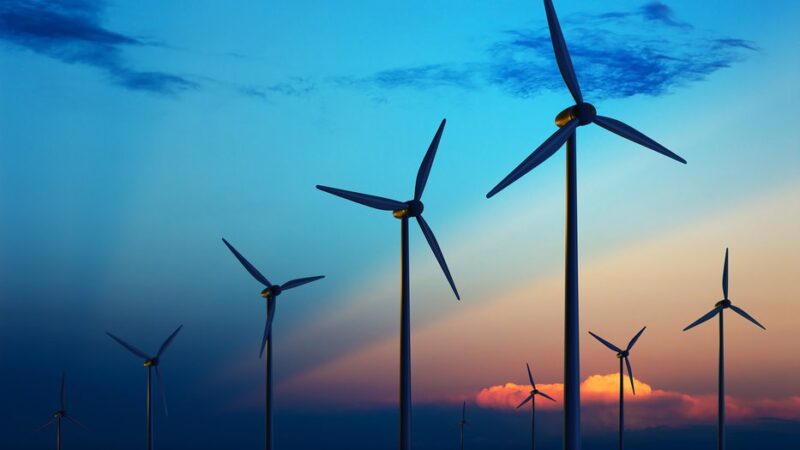

Wind energy, generated by converting wind currents into power, is another robust renewable source. Wind turbines, both onshore and offshore, capture kinetic energy from the wind, converting it into electricity. This form of power generation is increasingly popular due to its low environmental impact and substantial energy yield.
The evolution of wind turbine technology has led to taller, more efficient designs capable of capturing higher-altitude winds. Nevertheless, wind energy’s variable nature requires complementary storage solutions or hybrid systems for consistency.
Hydropower
Harnessing the movement of water, hydropower is one of the most established forms of renewable power. From small run-of-the-river systems to massive dams, water’s kinetic energy is converted into electricity. This method’s efficiency and reliability make it a significant contributor to the global renewable energy mix.
Despite its benefits, hydropower can have ecological impacts, such as affecting water ecosystems and displacement issues. Thus, there’s a growing focus on developing less invasive hydropower technologies.
Geothermal Power
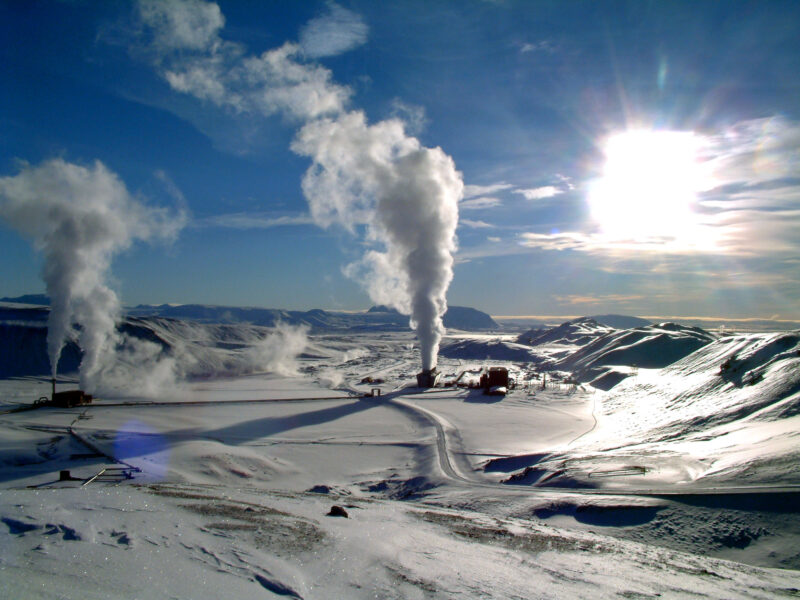

Tapping into the Earth’s internal heat, geothermal power stations produce electricity with minimal carbon footprint. This constant heat source offers a more consistent power supply compared to other renewable sources. Geothermal plants harness steam from the earth to drive turbines, generating power.
Geothermal energy’s reliance on specific geological conditions limits its widespread application. However, ongoing research aims to expand its feasibility to more regions.
Organic Materials as Fuel
Biomass energy involves using organic materials, such as plant matter and animal waste, to produce electricity, heat, and even fuel. This process often involves combustion, though other technologies like anaerobic digestion and gasification are also used.
The sustainability of biomass energy depends on balancing production with ecological and social impacts, such as land use and food security concerns.
Tidal and Wave Energy
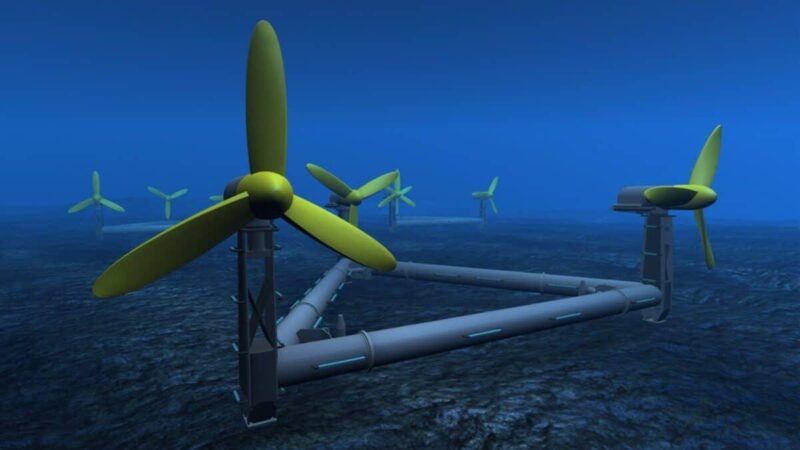

The ocean’s tidal movements and waves are potent, untapped sources of renewable power. Tidal energy, harnessed from the rise and fall of tides, involves turbines in tidal streams or barrages across estuaries. Wave energy, on the other hand, utilizes the surface motion of seas and oceans.
These technologies, still in developmental stages, promise significant power generation with minimal environmental impact. However, their success hinges on overcoming technical, ecological, and cost challenges.
Sustainable Living
Sustainability in daily life is not just about choosing renewable power; it involves a holistic approach to living. Reducing waste, conserving water, and opting for sustainable transportation are integral. Embracing energy-efficient appliances, minimizing plastic use, and supporting local, sustainable agriculture also contribute to a healthier planet.
Energy Efficiency: Maximizing Power Usage

Energy efficiency is a critical component of a sustainable lifestyle. It involves optimizing our power consumption to reduce waste and increase effectiveness. This can be achieved through various means, such as improving insulation in homes to reduce heating and cooling needs, using LED lighting which consumes less electricity, and choosing energy-efficient appliances that require less power to operate.
Incorporating smart technology in homes and businesses can also play a significant role. Smart thermostats, for instance, adjust heating and cooling based on occupancy and preferences, minimizing unnecessary power use. Similarly, energy management systems can monitor and control energy consumption in larger buildings, leading to significant reductions in power usage.
Green Transportation: Moving Towards Sustainability
Green transportation is another crucial aspect of a sustainable lifestyle. This involves reducing reliance on fossil-fuel-powered vehicles and embracing cleaner alternatives. Electric vehicles (EVs) are at the forefront of this shift, offering a zero-emission mode of transportation when powered by renewable sources. The expansion of EV charging infrastructure and advancements in battery technology are making EVs more accessible and convenient.
Beyond personal vehicles, promoting public transportation, cycling, and walking can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of our daily commutes. Cities around the world are developing more bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly zones, making these sustainable modes of transportation more viable.
Sustainable Diet: Eating for the Planet

Our dietary choices have a profound impact on the planet. A sustainable diet focuses on reducing meat and dairy consumption, which are resource-intensive to produce, and prioritizing plant-based foods. Eating locally-sourced and organic produce can also reduce the environmental impact of food production, as it often involves fewer chemicals and shorter transportation distances.
Reducing food waste is equally important. Planning meals, storing food properly, and using leftovers can significantly cut down the amount of food that ends up in landfills, where it generates greenhouse gases.
Community Engagement: Collective Action for Change
Sustainability is not just an individual pursuit; it thrives on community involvement. Engaging with local communities to promote renewable power and sustainable practices can have a multiplying effect. This can involve participating in community gardens, which foster local food production, or joining local initiatives for clean-up drives and recycling programs.
Advocating for policy changes at local and national levels is also crucial. Supporting policies that promote renewable power sources, green transportation, and sustainable agriculture can lead to systemic changes that make sustainable living more attainable for everyone.
Final Thoughts
The journey to a sustainable future is multifaceted, involving a mix of renewable power sources and lifestyle changes. While challenges remain in fully realizing the potential of renewable sources, technological advancements and policy support are paving the way. Simultaneously, individual and collective actions in adopting sustainable practices play a vital role.
Related Posts:
- Influencer's Handbook: Monetization Strategies for…
- Quick Tips to Naturally Increase Fertility and Boost…
- How to Spend a Winter in Norway with Joy and Wonder:…
- Revolutionizing Your Digital Space: 10 Tips for…
- 10 Tips for Making the Right Choice between Glass…
- How to Sell Your Car Safely: 9 Tips and Advice for a…